- info@jodhani.in
About Diamond
You are here: Home \ Diamond

When purchasing a diamond, you will hear mention of the “4Cs”. This method of evaluating stones relies on four factors:cut,color,clarity, and carat weight. The 4Cs offer a useful starting point. But evaluating a diamond merely by the 4Cs is like describing your beloved on the basis of height and eye color. Just because two diamonds look the same “on paper” does not mean the actually look the same.
We selects diamonds for our engagement rings according to according to a more complex set of criteria, applying a high level of connoisseurship which cannot be translated into any gemological report.
Diamonds are not manufactured on an assembly line.
Diamonds are not interchangeable.They are unique

The beauty of a diamond depends on how well it has been cut more than anything else. Understanding the cut of a diamond begins with the stone’s shape. However cut as a value factor that determines the beauty of a stone refers to a stone’s proportion, symmetry and polish. Although nature determines a Trough diamond’s clarity, carat weight and color, the hands of master craftsmen release its fire, brilliance and scintillaion. When a diamond is cut to exacting proportions – neither too deep nor too shallow – light will reflect inside the stone from one mirror-like facet to another and reappear through the top of the stone, making it seem to radiate from within.
Our diamonds are cut to exacting proportions that maximize the beauty of the stone, even when such precision requires sacrificing more of a rough diamond’s weight.
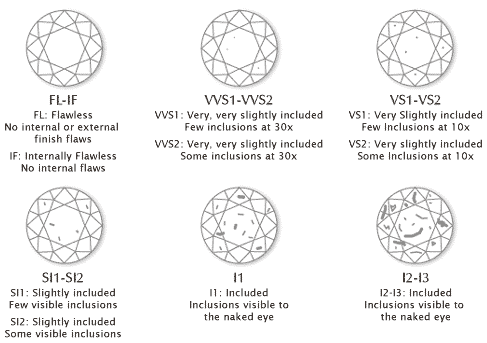
Virtually all diamonds contain identifying characteristics, most of them too small to be seen with the unaided eye. These "inclusions" are nature’s birthmarks; when viewed using magnification they like tiny crystals, clouds or feathers.
To determine a diamond’s clarity grade, a gemologist will consider the size, number, position, color and general of any incusions. Diamonds exhibitind no such inclusions are categorized as flawless (FL) or internally flawless (IF).
In general, the greater the number and size of inclusions within a diamond, the lower its clarity grade. Our diamonds are selected from the top clarity grades;any inclusions only become visible under 10x power magnification

Diamonds are transparent, most display barely perceptible hints of color. The less color in a diamond, the more rare it is.
Diamonds are graded ona color scale from D through Z, based on their degree of colorlessness. Harry Winston selects colorless diamonds from the top three color grades D, E, F for our enagagement rings. These are the most rare and, therefore, the most valuable.
Fancy colored diamonds are an exception and are also much sought after due to their extreme rarity – particularly yellows, pinks and blues. Their quality is judged by the intensity of their hue, and unlike diamonds, the more color, the rarer.

A carat (ct.) is the unit of measurement specifically used to describe the weight of a diamond (or other gemstones). Its name comes from the carob seed – a small seed with a typically uniform weight that early gem traders used as counterweights for balancing their scales, according to the GIA. A single carat is equivalent to 0.2 grams, or 200 milligrams, and is divided into 100 points.AA certified diamond that comes with a grading report will indicate the exact carat weight to the nearest hundredth of a carat, in decimal format. A 1-carat diamond has 100 points (1.00) while a ¾ carat stone has 75 points (0.75). Carat weight in pre-set jewelry is typically described as a fraction (e.g. ¾ carats) and has an equivalent decimal range (¾ carats = 0.69 – 0.82 points). The following table correlates fractional sizes with their decimal equivalent:
CARAT FRACTIONS
- 1/10
- 1/8
- 1/7
- 1/6
- 1/5
- 1/4
- 1/3
- 3/8
- 1/2
- 5/8
- 3/4
- 7/8
- 4/4
- 6/4
- 8/4
- 12/4
DECIMAL EQUIVALENT
- 0.09-0.11
- 0.12-0.13
- 0.14-0.15
- 0.16-01.7
- 0.18-0.22
- 0.23-0.28
- 0.29-0.36
- 0.37-0.44
- 0.45-0.58
- 0.59-0.68
- 0.69-0.82
- 0.83-0.94
- 0.95-1.49
- 1.50-1.99
- 2.00-3.99
- 3.00-3.99
The carat is probably the most familiar of the 4C terms because it is the easiest one to understand just by looking at the stone. However, people often mistakenly assume that a diamond’s size is synonymous with its weight, though that’s not necessarily true. The way a diamond is cut can actually obscure its size and true weight. The following diagram shows the relative size of carat weights for a diamond that is cut to the same proportions:Note: Diamond illustrations show relative size, not actual size.